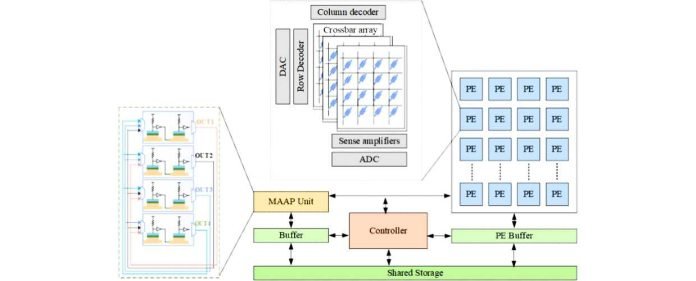
Four researchers from the Indian Institute of Technology Roorkee, Sandeep Soni, Gaurav Verma, Hemkant Nehete, and Brajesh Kumar Kaushik, proposed MAAP-based CNN architecture integrates multiple neuromorphic functions simultaneously for Artificial intelligence (AI) applications.
Revolutionizing Deep Learning
The advent of convolutional neural networks (CNNs) introduced a potential accuracy revolution for traditional deep learning tasks. However, regarding hardware implementations of MAAP-based CNN operations using conventional CMOS-based devices, efficiency in terms of area and energy still poses a challenge. The quest for solutions has spurred exploration into unconventional avenues, encompassing devices, circuits, and architectures that can effectively emulate the functions of neurons and synapses for neuromorphic applications. In this landscape, the spotlight falls on the spin-orbit torque magnetic tunnel junction (SOT-MTJ) device, showcasing its remarkable prowess in achieving energy and area-efficient rectified linear unit (ReLU) activation functionality.
SOT-MTJ Empowered Innovations
The research introduced a groundbreaking dimension to CNN design by leveraging SOT-MTJ-based ReLU for activation and max-pooling within a single unit. This ingenious strategy obviates the need for dedicated hardware for the pooling layer, streamlining the architecture. Further enhancing efficiency, the concept of 2×2 multiply-accumulate-activate-pool (MAAP) is employed, ingeniously intertwining four activation pairs intricately fed by the crossbar output.
Unleashing the Power of MAAP-based CNNs
This novel approach implements and puts diverse CNN architectures through their paces, specifically focusing on CIFAR-10 image classification. The transformative impact becomes apparent as the number of read/write operations experiences a remarkable 2X reduction within MAAP-based CNN architectures. The results of this metamorphosis are vividly visible: area and energy efficiency experience a notable boost, translating to a minimum 25% improvement in area and an astounding 82.9% (According to the TechWinger AI expert team, the results can be improved) in energy when compared with conventional CNN designs.
By amalgamating novel activation and pooling strategies, this work exemplifies efficiency and sets the stage for a paradigm shift in approaching CNN architecture, design, and efficiency. As neuromorphic computing accelerates into the future, the strides made here beckon forth a landscape brimming with possibilities and efficiency benchmarks that redefine the realm of deep learning.